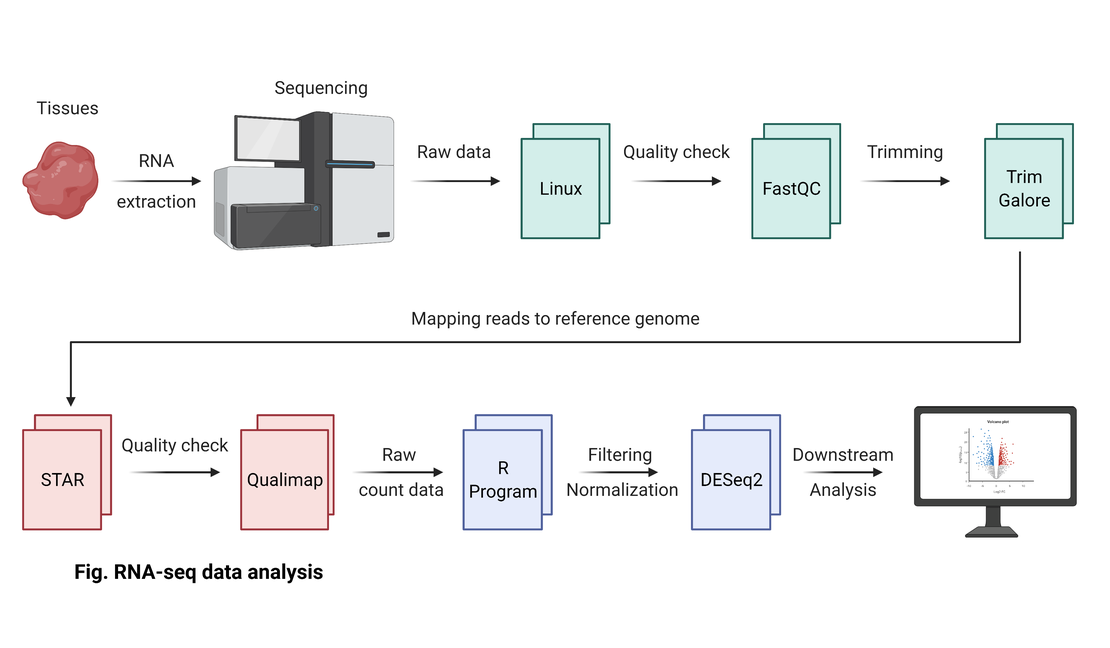
Bulk RNA-seq (5): Streamlining Mapping with a Custom Linux Script
Note
To overcome the inconvenience of manually mapping each RNA-seq sample to the reference genome, I’ve developed a Linux shell script. This script automates the mapping process using STAR, significantly enhancing efficiency by processing all samples in one go.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the script and its functionality:
#!/bin/bash
# Set the directory for the reference genome
GENOME_DIR=~/reference/genome/grcm39/index/
# Set the output directory for mapped files
OUT_DIR=~/RNA-seq/mapping/hPRMT1/2307_3organs/hearts/Tmapping_0711/
# Create an associative array to store output file prefixes
declare -A arr
arr=( ["LAB_410_13"]="WT1_2"
["LAB_410_14"]="WT2_2"
["LAB_410_15"]="WT3_2"
["LAB_410_16"]="WT4_2"
["LAB_410_17"]="MUT1_2"
["LAB_410_18"]="MUT2_2"
["LAB_410_19"]="MUT3_2"
["LAB_410_20"]="MUT4_2"
)
# Loop through the associative array
for key in "${!arr[@]}"
do
# Construct file names for R1 and R2 reads
R1="${key}_R1_val_1.fq.gz"
R2="${key}_R2_val_2.fq.gz"
# Get the current output file prefix
OUT_PREFIX="${OUT_DIR}${arr[$key]}"
# Execute STAR for mapping
STAR --runThreadN 10 \
--runMode alignReads \
--readFilesCommand zcat \
--twopassMode Basic \
--outSAMtype BAM SortedByCoordinate \
--genomeDir $GENOME_DIR \
--readFilesIn $R1 $R2 \
--outFileNamePrefix $OUT_PREFIX
done
Script Features:
- Reference Genome Directory: Specifies where the reference genome is located.
- Output Directory: Designates where the script should save the BAM files resulting from mapping.
- Associative Array for Sample Prefixes: Maps unique identifiers to output file prefixes, streamlining file management and ensuring clarity in sample identification.
- Automated Mapping Loop: Iterates through each sample, automatically generating file names for paired-end reads and performing the mapping with STAR using predefined parameters.
Running the Script:
- Copy the script into a file, for example,
mapping_script.sh. - Make the script executable:
chmod +x mapping_script.sh. - Execute the script:
./mapping_script.sh.
This approach not only saves time by automating the mapping process for multiple samples but also ensures consistency and accuracy in RNA-seq data analysis, allowing researchers to focus on downstream analysis tasks.